Figure: NF kappa-B signalling
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Introduction
- the size of the proteins are not an indication of the molecular weights or amino acid lengths.
- all possible pathways do not necessarily all occur in one cell.
- rectangular boxes on TNFR & Tradd represent death domains.
- NIK (NF kappa B inducing factor) associates with traf-2 or traf-6 & IKAP, IKK-alpha IKK-beta of IKK complex.
- both NIK & MEKK1 can phosphorylate IKK-alpha & IKK-beta.
- IKK complex phosphorylates I-kappa-B-alpha or I-kappa-B-beta which targets it for degradation, unmasking the nuclear localization signal in RelA of the NF-kappa-B complex.
- I-kappa-B-alpha phosphorylation of S32 & S36 leads to ubiquitination of K21 & K22 leading to degradation[7].
- KBRAS-1 & KBRAS-2 associate with IkB when complexed with NFkB & slow down degradation of IkB.
- there is also a separate PMA inducible IKK complex containing IKK-epsilon, but not IKK-alpha, IKK-beta, or IKK-gamma.
- T cell receptor also activates the PMA inducible IKK complex.
- p38MAPK affects NF kappa B dependent gene transcription through regulating activation of TFIID (TBP)
- inhibition of phosphorylation of TFIID (TBP) reduces its binding to the TATA box & interaction with p65 subunit of NF kappa B[6].
- NIK also activates MEK & ERK1/2 which act upstream of & regulate NF kappa B DNA binding activity[8].
- PDGF & PMA can activate NAK/TBK1 which acts upstream of I kappa B[7].
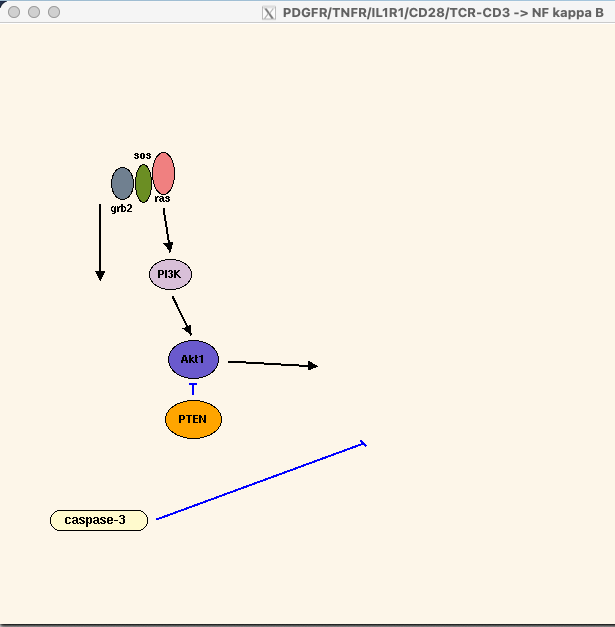
- PDGF through ras & PI3K can activate Akt1 kinase (PKB) which associates with & mediates IKK-alpha phosphorylation at T23 & is necessary for NF kappa B activation by TNF[5][9].
- Akt1 activation of NF kappa B also occurs through transactivation potential of p65 subunit[11].
- in TNF-alpha induced pathways, NF kappa B shows anti-apoptotic activity.
- proteolysis of IKK beta by caspase-3 interferred with IKK activation & promotes TNF-alpha apoptosis[10].
- PTEN blocks Akt1 kinase activity & blocks ability of TNF to stimulate transactivation domain of p65 subunit of NF kappa B (probably through blocking Akt1 activity but not affecting IKK degradation of IKB)[11]
References
- ↑ Stancovski & Baltimore. Cell 91:299-302, 1997
- ↑ Scheidereit. Nature 395:225-6, 1998
- ↑ Peters et al. Molecular Cell 5:513-22, 2000
- ↑ Ryam et al. Nature 404:892-7, 2000
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Ozes et al. Nature 401:82-5, 1999
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Carter et al. J Biol Chem 274:30858-63, 1999
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Peters & Maniatis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1471: M57-M62, 2001
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Dhawan & Richmond. JBC in press Dec. 28, 2001
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Romashkova & Makarov. Nature 401:86-90, 1999
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Tang et al. Molecular Cell *:1005-16, 2001
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Mayo et al. JBC Jan 17, 2002