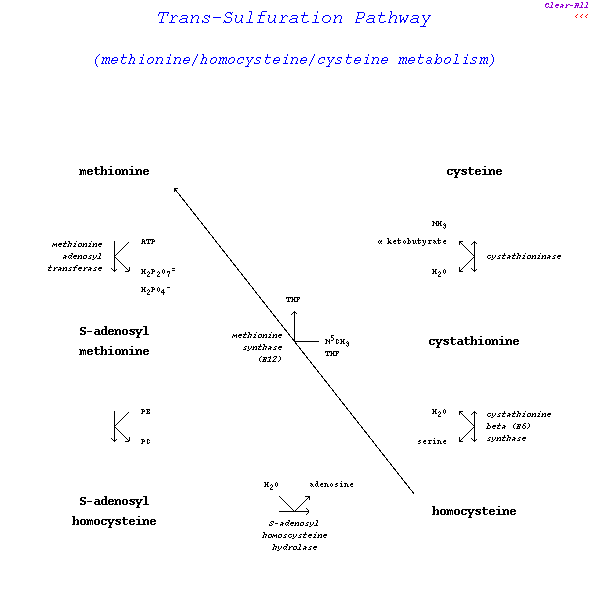
Figure: trans-sulfuration pathway
Introduction
The trans-sufuration pathway serves to interconvert the sulfur amino acids cysteine, homocysteine & methionine & also functions in the activated methyl cycle.
S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) is the major donor of methyl groups in mammals.
N5-methyl tetrahydrofolate (THF) can can donate methyl groups, but its transfer potential is insufficient for most biosynthetic methylations.*
The methyl group on methionine of SAM is activated by the positive charge of the adjacent sulfur atom.
Methyl acceptors from SAM include phosphatidylethanolamine, catecholamines & lysine residues of proteins in the biosynthesis of carnitine.
* Note that N5-methyl THF is the methyl donor in the conversion of homocysteine to methionine.
* This results in formation of THF.
* The THF is in turn used by serine hydroxymethyltransferase for the formation of N5,N10-methylene-tetrahydrofolate used by thymidylate synthase in the biosynthesis of TMP (thymidine monophosphate), a precursor for DNA synthesis.
Methionine synthase catalyzes a vitamin B12 (methylcobalamin)-dependent reaction.
Regeneration of tetrahydrofolate is essential for activity of thymidylate synthase & DNA synthesis.
Vitamin B12 plays no other role in DNA synthesis.
An alternate reaction catalyzed by betaine-homocysteine methyltransferase also catalyzes homocysteine to methionine (see homocysteine).
Serine hydroxymethyltransferase catalyzes formation of 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate & glycine from serine & tetrahydrofolate.
The methylenetetrahydrofolate is, in turn used by thymidylate synthase in the biosynthesis of dTMP from dUMP.
Biochemistry
- methionine metabolism 1
- enzyme methionine adenosyltransferase
- substrate methionine + ATP
- product S-adenosylmethionine + H2P2O7-2 + H2PO4-
- methionine metabolism 1b
- methionine metabolism 2
- enzyme adenosylhomocysteinase
- substrate S-adenosylhomocysteine
- product homocysteine + adenosine + H2O
- methionine metabolism 3
- enzyme cystathionine beta-synthase
- substrate homocysteine + serine
- product cystathionine + H2O
- methionine metabolism 4
- enzyme cystathioninase
- substrate cystathionine))
- product cysteine + alpha-ketobutyrate + NH3
- methionine metabolism 5
- enzyme methionine synthase
- substrate homocysteine + 5-methyltetrahydrofolate
- product methionine + tetrahydrofolate
- methionine metabolism 6
- methionine metabolism 7
- methionine metabolism 8
- enzyme betaine homocysteine-S-methyltransferase
- substrate homocysteine + betaine
- product methionine + dimethylglycine
References
- ↑ Ref: Stryer Biochemistry WH Freeman & Co, New York, 1988 pg 582-84